What types of electronic devices are part of your daily life? They could be smartphones, computers, laptops, tablets, cameras, and some other electronic gadgets. A common component that these devices share is their reliance on Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) to function. Among the various types of PCBs, Flexible PCB stand out for their unique properties and applications. In this blog, we will look closely at flex PCB from its definition and construction to its types and applications.
What Is Flexible PCB?
A flexible PCB refers to a type of circuit board that is designed to bend, twist, and conform to different shapes without losing functionality. It differs from traditional rigid PCBs in that it uses a flexible polymer material, such as polyimide or polyester, as the base substrate instead of rigid fiberglass. The conductive copper traces are laminated onto this flexible polymer base layer, creating a thin and bendable circuit board. The absence of rigid reinforcement allows the flexible PCB to dynamically flex, twist, and contort during operation, making it suitable for applications where space is limited, weight is a concern, or the PCB needs to fit into tight spaces or around curved surfaces.
Flex PCB: Construction and Materials Used
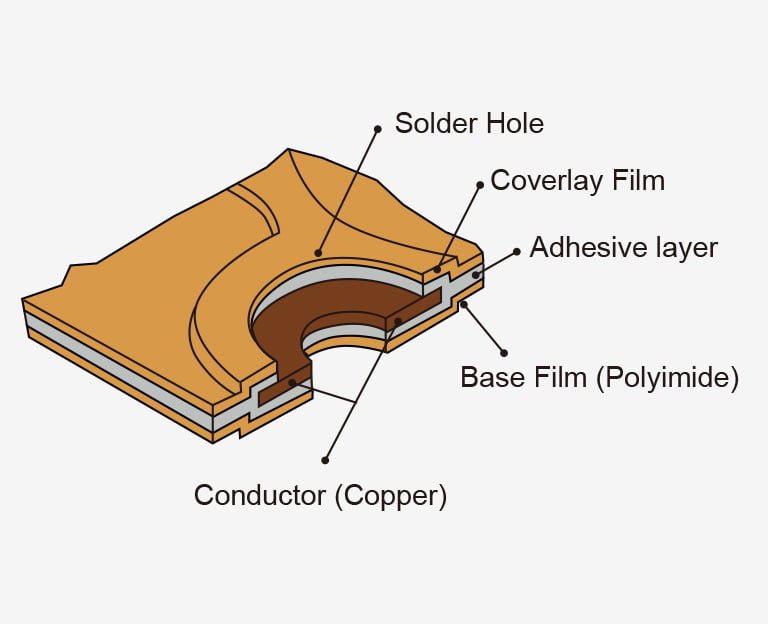
Flexible PCB mainly consists of the following layers:
- Dielectric Flexible Substrate
The foundational dielectric layer is essential for constructing the conductive paths. Therefore, selecting an appropriate material for the flexible substrate is crucial. Common options include Polyimide, Polyester, PTFE, and Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP). Among them, Polyimide is the most widely used flex substrate material due to its superior durability, thermal characteristics, and advantageous cost-to-performance ratio.
- Conductive Layer
The conductive layers are made up of copper foil or copper cladding laminated onto the substrate. These layers are etched to form the desired circuit patterns, including traces, pads, and vias. Copper is the most popular material for conductive layers as it is cost-effective. Some other choices include Silver Ink, Constantan, Carbon, Aluminum, and Inconel.
- Adhesive Layer
It firmly attaches the conductor metal onto the substrate. You will have to be very choosy while selecting adhesive materials. There are different adhesives material available for circuit boards including Epoxy, Pressure Sensitive Adhesives, and Acrylic.
- Overlay
The overlay is applied on the top of the flex circuit and its role is to safeguard the copper traces from adverse factors such as moisture, dust, and chemical contaminants. It can effectively prevent problems such as electrical short circuits. The material from which the overlay is made is typically polyimide, liquid photoimageable solder mask, or other dielectric materials.
- Stiffener
In certain situations, an additional stiffening material may be added to specific regions of the flexible printed circuit board. The purpose of this stiffener is to impart rigidity and structural support where it is required. Commonly utilized stiffening materials include adhesive-backed polyimide or FR-4 laminates.
Different Types of Flex Circuit Boards
There are 4 major types of flexible circuit boards available in the market. Here are as follows:
Single-Sided Flexible Circuit
It is one of the most common designs of circuits. There are several reasons behind its popularity. For example, they are the least expensive. They contain highly effective variants for different flex applications.
Double-Sided Flexible Circuit
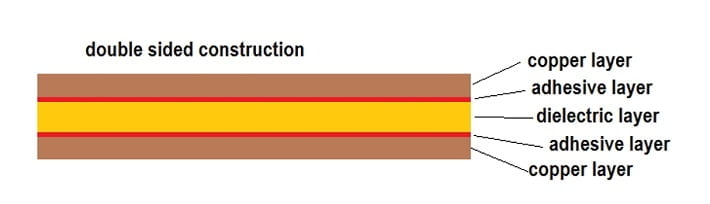
It is the second most common design for flex printed circuits. It is useful for all those applications that require high-density interconnection of circuits. Unlink single-sided circuitry, it features two metal layers connected with a plated-through hole. A standard double-sided circuit contains successive layers of adhesive and cover film on both sides of a base film.
Multilayer Flex PCB
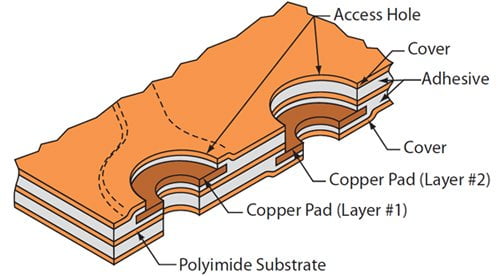
Multilayer flex circuits consist of three or more layers of conductive materials separated by insulating dielectric layers. They are more expensive than other PCB types due to the complexity of their construction. But these boards offer several advantages over their single or double-layer counterparts such as enhanced electrical performance, advanced functionalities, and improved mechanical robustness.
Rigid-Flex PCB
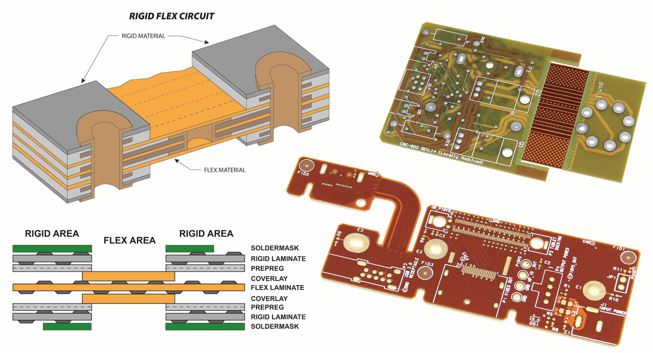
As the name suggests, it is a hybrid configuration that is a combination of both rigid and flexible printed circuit boards. The rigid portion supports all components and reinforces connectors. Meanwhile, the flexible section provides the whole connectivity for different rigid sections. Due to their reliability, strength, and flexibility, they are popular in applications such as military, aerospace, automotive and commercial electronics.
The Applications of Flexible PCB Board
When it comes to reliability, maximum adaptability and flexibility, flex PCB is extremely useful. Here are some most important applications of flexible circuit boards:
Flexible PCBs in Computer Electronics
Several main components of the computer rely on flex circuitry for proper operation. For example, to keep up with the high speeds, the components in hard drives require to be flexible. While utilizing hard drives for a long time span, it can get hot. It means circuit boards should be capable to withstand high temperatures. This is where flex PCB comes in. Likewise computers, you can find flexible circuit boards in other electronic gadgets, such as gaming systems, televisions, and printers.
Flex Printed Boards in Automotive Electronics
The majority of automotive electronic hardware uses flexible circuits. For example, engine management units or computers and airbag controllers use Flexible PCBs. We can also find flex PCB boards in Dash systems, anti-lock braking systems, and instrument panels. This preference stems from the unique ability of flexible PCBs to conform to irregular shapes and compact spaces, eliminating the need for bulky cable ties or connectors.
Flexible PCBs in the Medical Field
Flexible printed circuit boards have significant importance in different medical and pharmaceutical applications. The most popular application of flex circuits is a swallowable camera, commonly known as PillCam. This camera helps doctors or medical professionals to have an accurate view of the human body. Moreover, flexible PCBs are used to create realistic prosthetic limbs. Researchers have introduced a technique to print circuitry onto flexible and organic material. This material is extremely smaller than typical flex printed boards so it can move naturally without damaging.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Flexible PCB
Likewise all other types of printed circuit boards, it also has pros and cons:
Advantages of Flexible PCBs
There are several pros of flex circuit boards as compared to conventional electrical connections. Here are some pros of flex-circuits:
- It completely eliminates mechanical connections.
- Having the capability to produce a strong and reliable signal.
- It tolerates a huge temperature.
- Due to its flexibility, it is not breakable easily that makes it reliable.
- You can easily bend and fold it, resulting in a smaller size.
- It covers a very small area due to its smaller size.
- Flex circuits are lightweight.
Disadvantages of flex circuit boards
There are a few disadvantages to this board. Here are some cons of flex-circuits:
- Although it is durable, the initial cost of this circuit board is quite high.
- It is extremely difficult to make any change in this circuit board after finalizing it.
- Its rework and soldering require a professional team of engineers.
When to Use Flexible PCB?
Flexible printed circuit boards consist of polyimide or something similar. They can tolerate extreme temperatures even between 200 and 400C. So it is important to use a flex circuit when developing high-temperature and density applications. For example, borehole measurements in different gas and oil industries, have good usage. Additionally, they are capable of withstanding high temperatures and offer strong resistance to chemicals, radiation, and UV exposure. So it is extremely useful for all such applications dealing with chemicals and so on.
Why Not Use Flexible PCBs Exclusively?
Despite the numerous advantages offered by flexible PCBs, including their versatility and adaptability, they have not completely replaced rigid PCBs. The primary deterrent is cost. Flexible PCBs typically incur higher production and material costs compared to their rigid counterparts. Consequently, many companies opt for flexible PCBs only in applications that specifically benefit from their unique properties. For general manufacturing and assembly processes, rigid PCBs are preferred to manage and reduce overall costs.
MOKO Technology produces different types of printed circuit boards at an affordable price. With our team’s extensive expertise, we carefully evaluate your application’s unique requirements to select the optimal printed circuit board type. Reach out to us to start your project now.