What Causes PCB Short Circuit and How Can You Detect It?

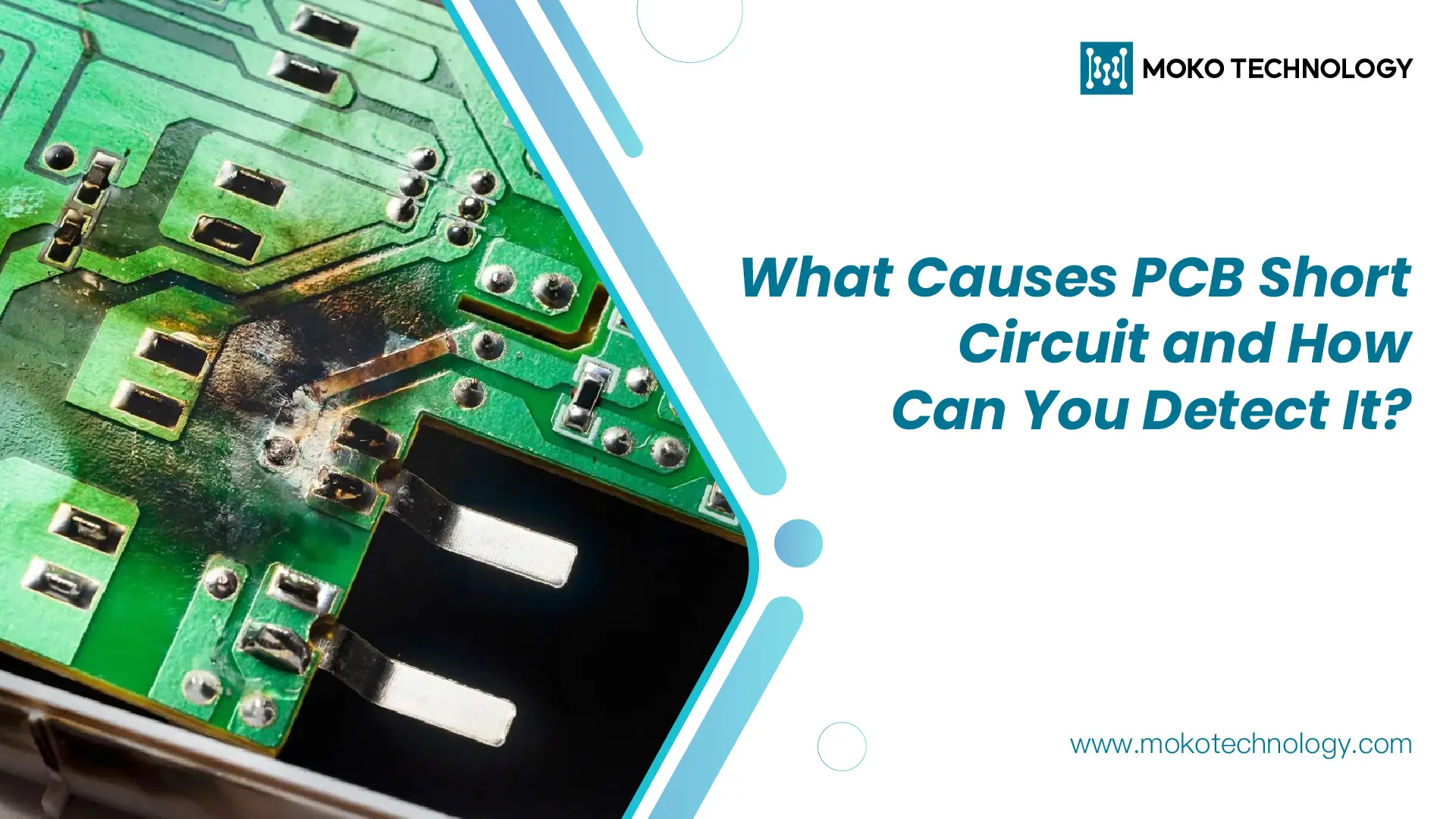
Have you ever had your smartphone suddenly turn into a hand-warmer or stubbornly refuse to charge? Or your computer acts up and suddenly shuts down without warning. Most probably, a PCB short circuit is at the root of the problem. A PCB short circuit is any undesirable connection between two points in an electronic circuit, through which electrical flow bypasses the normal current path. This can be a real headache, making the electronic products fail to function properly or even damaging the whole device. Therefore, it’s very important to detect it timely. In this blog, we will guide you through causes of PCB board short circuit, and methods to detect and avoid this issue. Let’s keep reading.
Common Causes of PCB Short Circuit
- External Contamination: Over time, dust and wetness harm PCBs. They bring in stuff that makes the board corrode, or add conductive material that changes how it works, leading to short circuits.
- Conductive Anodic Filamentation (CAF): Salts or metal bits stuck in PCB layers can cause trouble. When voltage is high, they start reactions that make conductive lines in the fiberglass. This is called CAF and can lead to short circuits in the PCB’s inner layers.
- Bad Soldering: If soldering goes wrong, short circuits can happen. Placing parts too near, not aligning them well, or using too much solder paste can create paths that short circuit. Further reading:Everything You Need To Know About PCB Soldering
- PCB Design Mistakes: Some short circuits happen due to design errors. Not checking the design well or simulating production can lead to bad layouts, no clearance between traces, or wrong part placement.
Key Methods to Find a Short Circuit in PCB
-
Inspecting Visually
Take a look at the PCB using a magnifying glass to check for any issues like solder connections between pins, copper areas that are not completely etched or tiny shorts. Visual inspection is usually the first step in pinpointing locations of short circuits.
-
Using a Multimeter
Utilize a multimeter to locate where the short circuit is physically located. Start from the power source and test each set of traces and PCB pads. They should show resistance readings. If you encounter readings it indicates there’s a circuit. Also test circuits as low readings between them could suggest bridging.
-
Employing a Thermal Camera
If accessible, employing a camera can be very helpful. Short circuits often cause heat generation. Power up the PCB. Utilize the camera to identify components or joints that are significantly hotter than others pointing towards where the short may be situated.
-
Checking Components Relative to Ground
In PCBs with a grounded via or plane you can check for shorts by placing one multimeter pin on ground and touching another on components. Low resistance readings might signify an interruption, in the power path although some components could naturally have resistance when connected to ground.
-
Checking Each Component Separately
To verify functionality test each component separately with a multimeter. Take resistance readings on pads and pins. Inspect connections, between components and the ground. Defective components may not be easily identifiable, through inspection.
-
Destructive Testing
As a last resort, physically take the PCB apart by removing components and re-running multimeter tests on the exposed pads. This may help identify the component or area that is causing the short circuit. Be aware that this is an extreme form of testing and should only be done as a last resort, since it may further damage the PCB.
How to Prevent PCB Short Circuit?
Prevention is a proactive measure that is suitable during the short circuit phenomenon at the design, construction, and operational stages of the PCB.
First, best practices will help the designer ensure that the separation and insulation among the conductors and other electrics are properly done. This way, there is no unwanted electrical bridge formation.
Secondly, after the PCB manufacturing and operations, ordinary maintenance and inspection are highly required. Regular cleaning should be done to remove dust, moisture, and other conductive particles. However, the appropriate tools and cleaning solution usage should be employed to avoid PCB damage.
Thirdly, testing and troubleshooting are also vital preventive measures. Multimeters can be very useful to identify incorrect connections or short circuits on a PCB. A systematic approach of testing from the power supply to various other components and connections can help catch potential problems before they become chronic.
Lastly, strong quality control during manufacture and following of industry standards and best practices substantially lowers the risk of short circuits. The manufacturer should also take into consideration environmental factors, such as providing proper shielding or enclosures to the PCBs to ensure that they are not affected by extraneous factors.
Further reading- PCB Shield: Types, Benefits, and Layout Tips
Final Thoughts
Prevention and detection of short circuits on a PCB are very important in ensuring reliability and longevity in electronic devices. A short circuit can be one of the many causes, from design problems or environmental factors, but the risk can be highly reduced with proactive measures. Following industry best practices in design, robust quality control at manufacturing, regular inspections, and maintenance are all very important preventative measures. Partnership in using an experienced professional like MOKO Technology is highly recommended for the best PCB manufacturing processes and the highest quality assurance. Their professionalism in PCB design, manufacturing, and quality control helps in minimizing the risks of a short circuit by delivering quality products.
Recent Posts
Impedance Matching: A Critical Factor in High-Speed PCB Design
Impedance matching has become a cornerstone of the signal integrity in the realm of high speed PCB…
How to Clean a Circuit Board Safely and Effectively?
It is important to learn how to clean a circuit board properly if you’re working…
Counterbore vs Countersink: Which to Choose for Your PCB?
When designing PCBs, selecting the appropriate type of holes for fasteners is crucial. And much…
PCB Copper Foil: Types, Properties & How to Choose
PCB copper foil is one of the most critical materials in the printed circuit board…
MOKO Technology Launches Vietnam Manufacturing Base in February 2025
Shenzhen, China - February 11, 2025 - MOKO Technology, a leading global electronics manufacturing service…
PCB Solder Mask: What It Is and Why Every Circuit Board Needs It?
While most people focus on the components and copper traces that make up PCBs, there's…


