The Essential Guide to PCB Heatsink Design and Selection

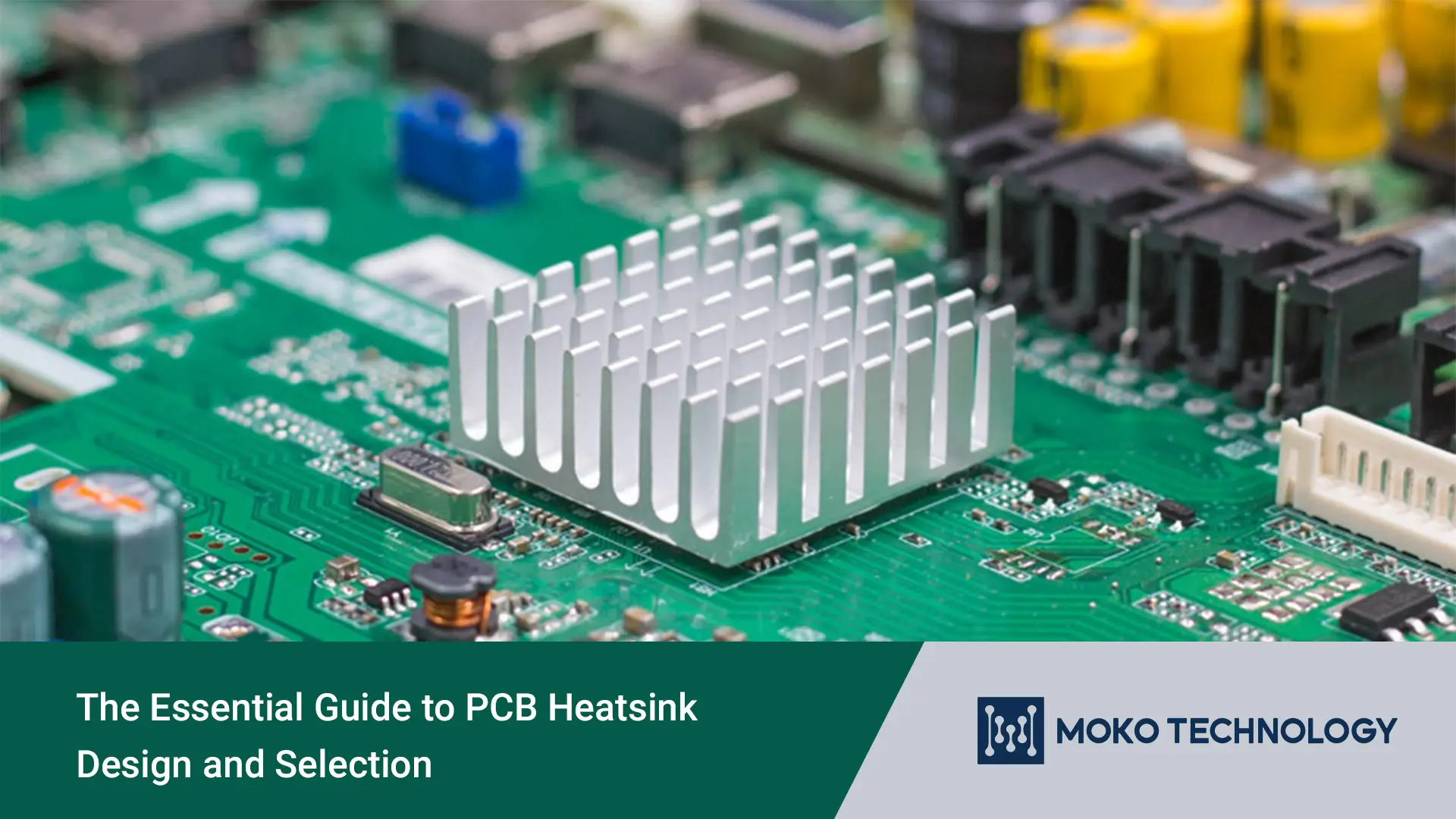
In today’s fast-paced world, electronic devices are rapidly shrinking in size while simultaneously expanding in functionality. To keep up with this trend, the design of PCBs must also evolve to be more compact. Just imagine a small circuit board carrying a variety of electronic components, all of them generating heat. If effective thermal management measures are not taken, the normal operation and service life of the equipment will be affected. One of the most effective ways to achieve optimal thermal management of the PCB is to connect a PCB heatsink. In this article, we will comprehensively introduce this important component, including its materials, working principles, application scenarios, selection guide, etc.
What Is PCB Heatsink?
PCB heat sink is a passive thermal management component, usually made of metal, a material with high thermal conductivity. Its primary function is to absorb and dissipate the heat generated by the electronic components on the printed circuit board through thermal conduction, thereby maintaining the device temperature within a safe operating range and preventing damage or performance degradation.
Materials of PCB Heatsink
Commonly used materials for making circuit board heat sinks are as follows:
- Aluminum: Aluminum is the most common heatsink material. It is lightweight and has relatively high thermal conductivity. More importantly, it is cheaper than other heat sink materials, so it is widely used.
- Copper:It has a higher thermal conductivity than aluminum, but comes with a higher cost. Therefore it is often used to manufacture heat sinks applied in high-performance applications.
- Aluminum alloys: Various aluminum alloysoffer improved mechanical properties and can be tailored to meet specific requirements for thermal conductivity, strength, and corrosion resistance.
- Graphite: Graphite, while not a metal, has a relatively high thermal conductivity and can be used in PCB heatsinks, particularly in applications where weight is a critical concern.
- Ceramics: It is particularly suitable in situations where electrical insulation is also a requirement, in addition to heat dissipation. Though ceramics generally do not conduct heat as well as metals.
Below we list a chart to compare these materials from different aspects:
| Material | Thermal Conductivity(W/mK) | Cost | Weight | Electrical Insulation | Common Applications |
| Aluminum | ~205 | Low | Light | No | General use, widely applicable |
| Copper | ~385 | High | Heavy | No | High-performance applications |
| Aluminum Alloys | Variable (~120-220) | Moderate | Light | No | Applications requiring specific mechanical properties |
| Graphite | ~150-400 (anisotropic) | Moderate-High | Very Light | NO | Weight-critical applications |
| Ceramics | Variable (20-200) | Moderate-High | Moderate | Yes | Electrical insulation required |
How Does PCB Heatsink Work?
The fundamental operation of a PCB heatsink hinges on the principle of heat conduction, where heat generated by PCB components is effectively transferred to the heatsink, a component designed specifically for this purpose. Components on a PCB often generate heat during operation, creating areas of high temperature. The heatsink, engineered to have low thermal resistance, acts as a thermal bridge, drawing this heat away from the components. It typically features a large surface area, often augmented with fins, to facilitate the efficient transfer of heat to the surrounding air.
Circuit Board Heat Sink Attachment Methods
PCB heat sinks can be mounted on the PCB in a variety of ways, including:
Thermal Adhesive: Simple and effective, thermal adhesives (paste or tape) provide a permanent bond, suitable for many applications but making future adjustments challenging.
Push Pins: Ideal for securing larger heatsinks, push pins offer a strong attachment through the PCB and are easier to remove than adhesives.
Clips and Brackets: These provide a secure, tool-free attachment that’s convenient for applications requiring heatsink removal or adjustment.
Screw Mounting: Offering a durable connection, screws require holes or standoffs on the PCB but make attaching and detaching straightforward.
Snap-Fit: For lighter heatsinks, snap-fit attachments allow for quick and tool-less installation and removal.
Thermal Epoxy: Similar to adhesives but offering a stronger bond, thermal epoxies are permanent and provide excellent thermal conductivity.
Solder Anchors: Used in high-reliability applications, soldering the heatsink directly to the PCB ensures maximum durability and thermal efficiency but is permanent.
Situations Where PCB Heatsink Are Used
When we design a PCB, how do we determine whether we need to use a heatsink? Below are situations where PCB heatsink are usually used:
- When circuit board design uses processors such as CPU, GPU and MPU, a heat sink is usually required.
- If there are power components such as power regulators, power amplifiers and power supplies, a circuit board heat sink is necessary. Because such components tend to dissipate more heat.
- When there are too many components on the PCB and are too dense, more heat will be generated. In this case, we also need to use a heat sink to reduce the temperature of the components.
- Consider whether a heat sink is needed based on the final application of the PCB. For example, when PCB is used in high temperature environment, a heat sink is also essential.
Tips for PCB Heatsink Design
Only by designing a proper heatsink can you achieve maximum thermal management. Here we provide some basic PCB heatsink design tips:
- Material Selection
Aluminum has lower weight and relatively low price, while copper offers superior thermal conductivity. Therefore, when selecting heatsink materials, we need to consider their features comprehensively including thermal conductivity, cost, weight, etc. - Surface Area Maximization
When designing a heat sink, you can increase the surface area of the circuit board heat sink by using fins or pins to enhance heat dissipation. This is because such a design allows more air to flow through the heat sink, thereby removing heat more efficiently. - Airflow Optimization
Design the heatsink layout and positioning to take advantage of natural or forced airflow within the device. The orientation of fins should align with air flow direction to maximize heat dissipation. - Space Constraint
Ensuring there is adequate space for mounting heat sink on PCB is crucial. For example, in scenarios where there is a height restriction, opting for low-profile heatsinks can facilitate efficient heat dissipation without breaching these spatial boundaries. - Simulation and Testing
After completing the heatsink design, we need to use thermal simulation software to predict the performance of the heatsink under various operating conditions, making sure that it can achieve the performance as designed.
Conclusion
A PCB heatsink enhances the reliability and longevity of electronic devices by efficiently dissipating the excess heat produced by components on the circuit board. Through this blog, we aim to share industry-leading practices in designing circuit board heatsinks, offering valuable insights for your projects. As an industry expert with many years of experience in the PCB field, MOKO Technology is proficient in the design and manufacturing of various PCBs. If you have other questions about PCB thermal management, or want to get high-quality PCB design services from us, please contact us now.
Recent Posts
Impedance Matching: A Critical Factor in High-Speed PCB Design
Impedance matching has become a cornerstone of the signal integrity in the realm of high speed PCB…
How to Clean a Circuit Board Safely and Effectively?
It is important to learn how to clean a circuit board properly if you’re working…
Counterbore vs Countersink: Which to Choose for Your PCB?
When designing PCBs, selecting the appropriate type of holes for fasteners is crucial. And much…
PCB Copper Foil: Types, Properties & How to Choose
PCB copper foil is one of the most critical materials in the printed circuit board…
MOKO Technology Launches Vietnam Manufacturing Base in February 2025
Shenzhen, China - February 11, 2025 - MOKO Technology, a leading global electronics manufacturing service…
PCB Solder Mask: What It Is and Why Every Circuit Board Needs It?
While most people focus on the components and copper traces that make up PCBs, there's…


