How Many Types of PCB Are There

Types of PCB
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) plays an important role in modern life that electrically connects and mechanically supports various electronic devices and components. From mobile phones and computers used every day to precision-crafted medical devices, automotive components, and industrial equipment, PCBs are everywhere. According to the applications of printed circuit boards, manufacturing materials, and manufacturing processes, PCBs are classified into a variety of types. Today, we will take a look at common types of PCB:
Single-sided PCB
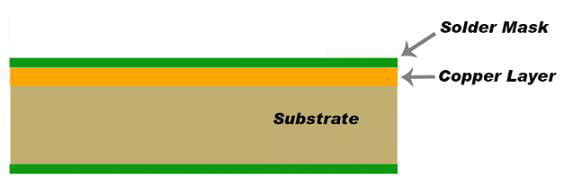
A single-sided PCB is one of the types of PCB and is made from a single layer of a substrate. Only one side of this substrate is coated with copper. In single-layer boards, we solder various components onto one side, which makes it easier to design and produce. Therefore, compare to other types of PCBs, they have lower costs and can be manufactured in a shorter time. Single-sided PCB is usually used in equipment such as calculators, printers, radios, and cameras that do not have high requirements for PCBs, and their working principles are relatively simple.

Double-sided PCB
Double-sided PCB has a substrate material like single-layer PCB, but the substrate is coated with copper on both sides. We can drill holes in double-layer boards to allow the connection between components on opposite sides. And this type of printed circuit board is normally used in applications that have intermediate complexity, typical examples include LEDs, amplifiers, UPS systems, HVAC systems, cell phone systems, vending machines, and car dashboards.


Multi-layer PCB
Multi-layer PCB refers to a printed circuit board with more than 2 layers and three or more conductive layers. And all the layers are placed by sandwiching them between layers of insulation to ensure that excess heat won’t damage the components. This type of PCB is suitable for a wide range of advanced electronic applications such as data storage, file servers, satellite systems, medical equipment, GPS technology, and weather analysis.
Rigid PCB
Rigid PCB, true to its name, is a type of PCB that cannot be twisted or folded. Its base material of it is a rigid substrate, so it has the properties of rigidity and strength. And it consists of many layers including a substrate layer, a copper layer, a solder mask layer, and a silkscreen layer. In addition, rigid PCB can be manufactured as single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layered based on the specific requirements. The applications of rigid PCB include GPS equipment, MRI systems, mobile phones, temperature sensors, and so on.
Flexible PCB
Flexible PCB is the exact opposite of rigid PCB. As the name suggests, these PCBs are very flexible and can move freely. Since flexible PCB needs flexible manufacturing material, therefore, they have a high manufacturing cost.
Flexible PCB offers many benefits that rigid PCBs are unable to offer. We can fold flexible PCB over their edges and wrap them around the corners. Their flexibility allows them to have lightweight and hence we can use them in small spaces.
We can also use flexible PCB in those areas which are subjected to environmental hazards. However, to achieve this, we have to manufacture them using waterproof, corrosion-resistant, and shockproof materials. This is something that the rigid PCB is not capable of.
Flex rigid PCB
This type of PCB combines the properties of both rigid and flexible PCB. These boards have multiple layers of rigid PCB attached to a number of flexible PCB layers. These boards have more benefits than those offered by flexible or rigid PCB alone. Flex-rigid PCB has a lower part count than conventional flexible or rigid boards. This is because we can combine the wiring options for both of them into a single PCB. When we combine the properties of flexible and rigid PCBs in the flex-rigid board then we get a reduced size, streamlined design, and lighter weight.
We mostly use flex-rigid PCB in those applications where weight and space are of prime concern. This includes digital cameras, automobiles, cell phones, and pacemakers.
Materials for PCB Manufacturing
The dielectric substrate is a major part of PCB which is either flexible or rigid. We use a dielectric substrate with a copper coating. We will now discuss some of the materials which we frequently use for manufacturing PCB.
FR is an abbreviation for Fire Retardant. FR4 is the most common glass laminated material for all types of PCB fabrication. FR4 is a composite material that is based on woven glass-epoxy compounds. It is very useful because it gives us excellent mechanical strength.
- FR-1 and FR-2
This material is based on phenol and paper compounds. We mostly use this material only for single-layer PCBs. FR2 and FR1 have the same properties, however, they have one difference which is glass transition temperature. FR2 has a lower glass transition temperature in comparison to FR1. We further divide these materials into halogen-free, standard, and non-hydrophobic.
- CEM-1
This material is a composite of phenol compounds, paper, and woven glass epoxy. We use this material only for single-layer PCB. We can use CEM-1 as an alternative to FR4, but CEM-1 is more costly than FR4.
- CEM-3
This material is white in appearance and we mostly use it in double-layer PCBs. It is based on glass epoxy compounds. CEM-3 is cheaper than FR4 so it is a good alternative. However, it has lower mechanical strength in comparison to FR4.
- Polyimide
We mostly use this material in flexible PCBs. It is based on rogers, kepton, and dupont. It has good felicity, electrical properties, high chemical resistance, and a wide temperature range. The operating temperature of this material is from -200 ͦC to 300 ͦC.
- Prepreg
It is a kind of fiberglass that is impregnated with resin. These resins are pre-dried, so they stick, flow, and completely immerse when heated. The adhesive layer of the prepreg gives it a comparable strength to the FR4.
There are many forms of this material that have varying resin content. These include Medium Resin (MR), Standard Resin (SR), and High Resin (HR). We choose between these according to the layer structure, required thickness, and impedance.
Conclusion
Different printed circuit boards have different characteristics and are suitable for different use environments, so before choosing a PCB, you need to understand each type of PCB and consider factors such as space size, and mechanical and electrical stability. MOKO Technology is a leading company in the field of Printed Circuit Boards. We specialize in all types of PCB and provide one-stop PCB solutions ranging from PCB design to manufacturing, PCB assembly, and testing. Feel free to contact us if you have any queries or if you want a quote.
Recent Posts
Impedance Matching: A Critical Factor in High-Speed PCB Design
Impedance matching has become a cornerstone of the signal integrity in the realm of high speed PCB…
How to Clean a Circuit Board Safely and Effectively?
It is important to learn how to clean a circuit board properly if you’re working…
Counterbore vs Countersink: Which to Choose for Your PCB?
When designing PCBs, selecting the appropriate type of holes for fasteners is crucial. And much…
PCB Copper Foil: Types, Properties & How to Choose
PCB copper foil is one of the most critical materials in the printed circuit board…
MOKO Technology Launches Vietnam Manufacturing Base in February 2025
Shenzhen, China - February 11, 2025 - MOKO Technology, a leading global electronics manufacturing service…
PCB Solder Mask: What It Is and Why Every Circuit Board Needs It?
While most people focus on the components and copper traces that make up PCBs, there's…


