The Essential Guide to PCB Controllers


PCB controllers enable the smarts in electronics of all types, from tiny wearables to industrial robots. These ingenious chips act as the brains of countless devices today. They perceive inputs using sensors, crunching numbers, and executing logic to make decisions. Controllers then direct other components to take action through signals. And with the rise of connected IoT devices, PCB controllers take on an increasingly vital role – their intelligence allows technology to sense, process, and respond.
For any aspiring electronics product designer or practicing engineer, having a working understanding of PCB controller capabilities is absolutely essential. Selecting the right controller IC and properly integrating it into a PCB design can make or break functionality. In this guide, we explain everything needed to successfully leverage PCB controllers. Let’s read on.
What Is a PCB Controller?
A PCB controller stands as an electronic circuit meticulously crafted to govern the functioning of a PCB board. It has one main job – to enable smooth, flawless operation between connected components on the circuit board. The controller also carefully manages the timing and transfer of control signals between different parts of the circuitry.
A typical PCB controller includes a microcontroller or microprocessor, input/output (I/O) interfaces, power regulation circuitry, and sometimes specialized components for specific applications. The microcontroller or microprocessor is the brain of the PCB controller, responsible for executing instructions and making decisions based on the input signals it receives. The I/O interfaces enable communication between the controller and external devices, sensors, actuators, or user interfaces. The power regulation circuitry ensures that the components on the PCB receive stable and appropriate power levels for their proper functioning.

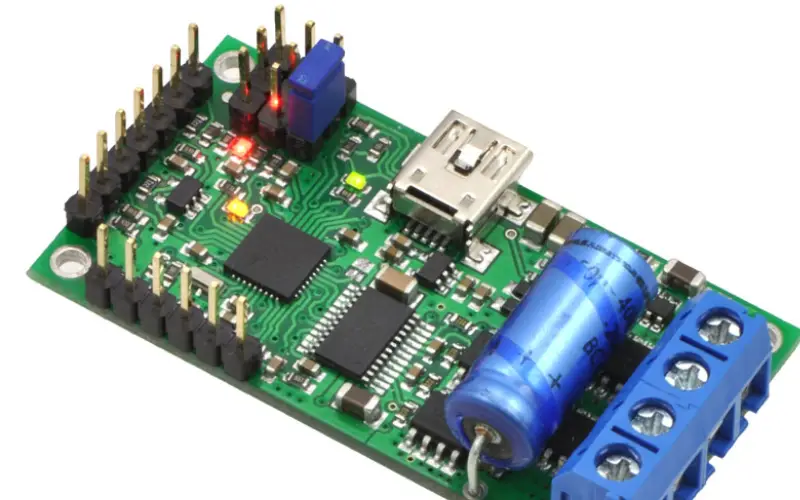
Key Functions of PCB Controllers
Data and Signal Processing: PCB controllers are responsible for processing data and signals received from various input sources. It coordinates the execution of commands, calculations, and logic operations required for the device’s functionality.
Component Communication: The controller board facilitates communication between different PCB components. It oversees the movement of data among memory units, power supplies, logic chips, sensors, actuators, and additional peripheral components.
Control Logic: PCB controllers contain control logic circuits that determine how the device responds to different inputs and conditions. It carries out pre-defined algorithms, takes actions based on those instructions, and oversees the precise timing and order of tasks.
Interface Management: PCB controller boards often have interfaces to interact with external devices, users, or other systems. These connections can encompass various elements like connectors, ports, and communication protocols that facilitate the interchange of data and control.
Error Detection and Handling: A PCB controller board monitors the device’s performance and detects errors or anomalies in the operation. It could incorporate methods to detect errors, incorporate safety measures, and adopt strategies for handling faults, all aimed at ensuring dependable and secure operation.
Applications of PCB Controllers
Consumer Electronics
PCB controllers are integral to consumer electronics like smartphones and gaming consoles, coordinating critical operations. These microchips manage power distribution, interface with touch displays, establish wireless connectivity and integrate sensors. Controllers orchestrate these subsystems, enabling seamless user experiences.
Automotive Industry
In automobiles, PCB controllers are crucial components enabling modern systems. They facilitate vital functions like powertrain management, safety mechanisms, and navigation. Through data processing and signaling, onboard controllers coordinate essential vehicle subsystems.
Industrial Automation
In manufacturing and industrial environments, PCB controllers manage processes such as robotics, assembly lines, and equipment automation. They enable machinery and sensors to operate at peak precision and productivity.
Medical Devices
The unassuming PCB controller enables vital medical devices to save lives. It allows complex equipment to acquire, analyze, and share patient data rapidly and precisely. Without the controller’s coordination, state-of-the-art healthcare technology would not be possible. Though concealed, this small component is an unsung hero safeguarding health behind the scenes.
Aerospace and Defense
PCB controllers are used in aircraft, satellites, and defense systems to manage navigation, communication, radar, guidance, and control systems. They ensure reliable performance in critical aerospace applications.
How to Design PCB Controllers?
Designing effective PCB controllers requires careful planning and execution across multiple stages. The key steps include:
- At the beginning, you should clearly identify the functional and performance requirements for your controller. Pinpoint its intended role and the specific tasks it should perform. Establish metrics like processing speed, memory, I/O, size constraints, and cost targets upfront.
- Then, select the optimal microcontrollerto serve as the core processing engine for your design. Evaluate different MCU options from vendors and choose one that aligns with your technical needs and specifications. Balance factors like architecture, clock speed, peripherals, power consumption, and development tools.
- With your MCU selected, design the layout and topology of the PCB itself. Decide on the board shape and footprint, number of layers, component placement, trace routing, and more based on your requirements. Aim for a compact yet modular layout that simplifies assembly and minimizes errors.
- Populate the board by carefully choosing complementary components like discrete passives, power regulation, external memories, connectors, and communication interfaces. Seek cost-effective parts that provide the necessary functionality without compromise.
- Extensively test both the bare PCB as well as the fully populated board. Verify connections, clocks, and power, and that any software running on the controller works as expected. Rigorously debugging at this stage prevents headaches later.
- Once the design is validated, proceed to assembling and solderingproduction units. Use consistent processes to ensure repeatable high-quality solder joints and minimize defects. Perform in-circuit testing for final quality control.
- Throughout this iterative process, segregate functional blocks, use quality components, facilitate removability and upgrades, and leverage design best practices. With thoughtful design and testing, your custom PCB controller can be successfully brought to production.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a PCB Controller
- Power Requirements
The power needs of a controller vary depending on its intended use. A controller meant for high-performance gaming computers needs abundant power to enable complex graphics and rapid computation. In contrast, a controller designed for a smart home assistant can function on minimal power due to a lower processing load. Picking the right power source is crucial for enabling any PCB controller to really strut its stuff.
- Memory Capacity
When it comes to PCB controllers, more memory means more brainpower for complex thinking. Like expanding a computer’s hard drive, additional memory gives the controller more room to crunch data and juggle multiple tasks. So, confirming sufficient memory capacity is vital for smooth operation.
- Compatibility
Verifying intercomponent compatibility is crucial. The controller cannot fulfill operational demands if incompatible with other system elements. Before purchase, ensure the controller’s technical specifications, including communication protocols, interfacing, and programming languages, align with the overall system architecture.
- Cost
When picking a PCB controller, remember that price and performance go hand-in-hand. A more expensive, high-end chip delivers advanced capabilities, while a budget model offers basic operation. The key is balancing capabilities against cost targets for your application.
- Dependability
The reliability of the controller stands as a critical aspect to take into account. It’s imperative that the controller effectively manages its assigned tasks without encountering any issues. Don’t gamble with an undependable, unstable controller at the helm of your system.
- Ease of Use
An intuitive, easy-to-use controller makes your job simpler compared to a complex beast of a component. Aim for a controller with straightforward documentation, clear programming interfaces, and robust development tools/support. Pick one you and your team understand inside and out. Simplicity and familiarity breed superior performance.
Closing Word
With their flexible processing, I/O, and connectivity, PCB controllers power the core functionality of countless electronic devices today. Understanding key capabilities like processing performance, memory, peripherals, power, and size enables matching controllers to application requirements. Following design best practices and a structured selection process ensures picking the right PCB controller to meet product needs while avoiding common pitfalls. With the knowledge provided in this guide, you are equipped to successfully leverage PCB controllers in your next design. If you still have doubts about it, reach out to experts in MOKO Technology, and we will make a response within 24 hours.
Recent Posts
Impedance Matching: A Critical Factor in High-Speed PCB Design
Impedance matching has become a cornerstone of the signal integrity in the realm of high speed PCB…
How to Clean a Circuit Board Safely and Effectively?
It is important to learn how to clean a circuit board properly if you’re working…
Counterbore vs Countersink: Which to Choose for Your PCB?
When designing PCBs, selecting the appropriate type of holes for fasteners is crucial. And much…
PCB Copper Foil: Types, Properties & How to Choose
PCB copper foil is one of the most critical materials in the printed circuit board…
MOKO Technology Launches Vietnam Manufacturing Base in February 2025
Shenzhen, China - February 11, 2025 - MOKO Technology, a leading global electronics manufacturing service…
PCB Solder Mask: What It Is and Why Every Circuit Board Needs It?
While most people focus on the components and copper traces that make up PCBs, there's…


