Printed circuit boards have historically been associated with a distinctive green color. However, as technology has advanced, PCBs have started to appear in various colors. This might lead you to wonder why printed circuit boards are available in various colors and how to choose the right one for your manufacturing needs. In this article, we will explore 7 main PCB colors, offering insights to help you select the most suitable one for your project.
Understanding PCB Colors
PCB colors come from the pigmented lacquer that is used to coat the boards instead of showing their natural copper color. The specific color of a PCB is determined by the color of the solder mask, which is a protective coating applied over the copper traces on the board. The purpose of the colored solder mask is to provide contrast with the metallic copper so that the traces can be clearly identified. Additionally, the solder mask gives the copper some protection against potential short circuits and also provides a layer of defense against physical wear and tear. Overall, PCB board colors serve functional purposes beyond just aesthetics – the colors allow for easier inspection of the boards and help shield the delicate copper traces.
Introducing 7 Types of PCB Colors
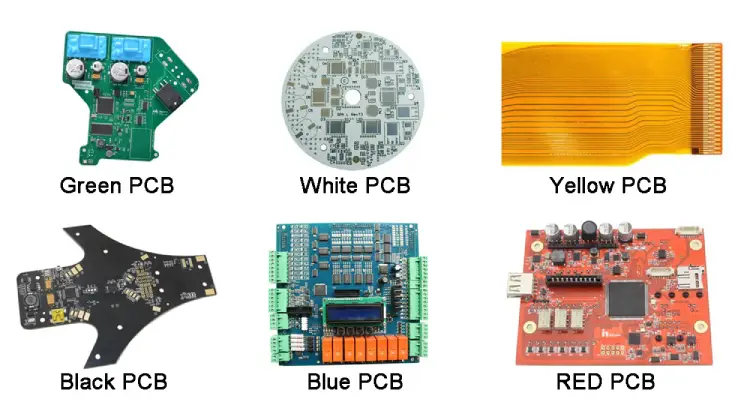
Green PCB
It is the most common solder mask color open for inspection. Due to its immense popularity, most people misunderstand that all PCBs are green in color. The green color gives transparency to the PCB, as it produces a bright contrast with a white-colored text, thus improving readability. Also, a green finish helps to minimize glare as it reflects less light. Therefore, green is an essential selection for PCBs that demand thorough scrutiny. Its color code is #008C4A.
Blue PCB
A blue solder mask is a perfect fit for heavy tag boards, as it offers a marked contrast with silkscreens. Although a blue circuit board is not as outstanding as black, green, or white, it is still ideal as it provides an excellent aesthetic choice. A blue PCB is perfect for mounting on an LCD. This is because it does not produce bright contextual colors and sharp contrasting edges. Its color code is #4990E2.
Yellow PCB
Yellow solder masks are catching a lot of attention globally. Like other new colors, yellow can easily help achieve different necessities, like style, visibility, and cleanliness. Although yellow is also an amusing color, it possesses a major hitch. Its color code is #F6A624.
White PCB
White PCB solder masks are gaining vast popularity as they appear clean in different environments. Even though white is sometimes referred to as bright show models, it is not ideal because of its affinity to hide traces. While working with a single overhead light, it is hard to inspect a white PCB board. Its color code is #ECECDF.
Red PCB
Most PCB manufacturers are slowly adopting red solder masks because of the specific benefits they offer. A red PCB board gives excellent visibility while at the same time well-defining contrasts for planes, traces, and empty spaces. A red background gives PCB silkscreen colors a sharp look. Its color code is #D0011B.
Black PCB
Black solder masks are becoming more popular in the same way as white solder masks. Black PCBs give less contrast, and they allow easy tagging when dealing with large components. Nevertheless, its major shortcoming is that it produces a small shadow when some of its components catch the light, making tracing more difficult. Black solder masks are unsuitable in applications that involve high heating since they can tarnish the silkscreen. Also, black PCB has a small conductivity as they feature a blend of carbon and cobalt. Its color code is #000000.
Purple PCB
The color purple is not commonly chosen for printed circuit boards. When it is selected, it is typically either for its distinctiveness or as a way to associate the board with a particular brand identity. If considering a purple PCB, it is important to evaluate the pros and cons. A potential downside is that the purple color costs more than other colors as most PCB manufacturers don’t offer it regularly.
Does PCB Color Matter?
Yes, the color of the PCB does matter for several important reasons:
- Different PCB board colors help provide a visual indicator of any revision changes or versions. Using distinct colors makes it easier to quickly identify different board revisions.
- The light absorption, reflectance, and transmission properties of different colors can impact the PCB assembly process. Certain colors may be selected to produce the desired contrast or brightness for a specific application.
- Alternative colors, beyond the traditional green, help with easier identification of lead-free assemblies. Distinct colors can quickly highlight lead-free boards.
- While color does not affect the underlying performance or resolution of the PCB itself, it does have an aesthetic and usability role. Color provides visual cues that influence the overall function and user experience of the assembled board.
Why the Green Color Is Primarily Used in PCBs?
The thought that the color of PCB is green always comes to mind whenever a circuit board is mentioned. So, for which reasons have green been the most preferred color over the years?
- Green minimizes visual fatigue
Most PCB manufacturers go for a dull shade of green as it isn’t as bright as red or pink. The color works well and for long on the board compared to more brilliant colors.
- Physical advantages
Another critical factor is contrast levels. Green gives visible differences in the PCB’s empty spaces, planes, and traces. Thus, making it easy to identify and sort a problem when doing repairs and inspections.
- Facilitate mass production
Since the green color has existed for a long time, PCB manufacturers have considered it the universal color code. This makes its production resources easily accessible and widely available in large volumes to PCB manufacturers.. The green PCB color RGB facilitates mass production as it is the color most people use.
- Less costly
When mass production is high, the accessibility also becomes more, thus considerably reducing the prices. Green is dominantly the standard color on most PCBs due to its affordable cost. Also, extra payments are needed when customizing the colors of a solder mask.
How to Select the Right PCB Colors?
When selecting the suitable PCB ink for your board, how should you choose the final color?
- PCB product considerations
While working on your solder mask, one of the natural colors that stands out is green. Usually, green has a 0.1 mm thickness layer; hence it is the thinnest of all coats. Also, green has been improved to work well with most PCB components and make repairs and assembling easier.
- Visibility
When selecting a solder mask color, it is crucial to choose a color that provides strong contrast with the board substrate and silkscreen markings. High contrast between the mask, board, and markings enables clear visibility. This visibility assists engineers and technicians in identifying potential issues like misalignment during soldering procedures.
- Aesthetics and Branding
Aesthetic appeal plays a major role in product design, so visual appearance should be considered when picking a PCB color. For instance, a black solder mask may be a suitable choice for a product with a modern, sleek intended style. Applying branded colors to solder masks can also help products maintain a cohesive look and enable identification of a brand. Companies can leverage PCB colors to align with branding strategies.
- Price considerations
Green is always top on the list when picking out the color of a PCB. Of all colors, green is the most reasonably priced and extensively accessible in vast quantities.
Final Thoughts
When selecting a PCB color, it’s important to weigh practical factors like cost, availability, and manufacturing considerations. Traditional green remains popular for its high contrast, reasonable pricing, and widespread availability. However, colors like white, red, blue, black, purple, and yellow offer distinct benefits ranging from improved inspectability to sleek, modern visual styles. With all PCB color options now readily accessible, companies can leverage solder mask hues to meet functional needs while also defining a unique product identity and style. By understanding the impacts of different color properties, PCB designers can make informed selections to balance practical considerations with branding objectives.